The world of Travel and Mobility Tech moves fast.
Every year, new trends make headlines, promising to redefine the industry—only for some to fade just as quickly as they emerged.
- Remember blockchain-based airline ticketing?
- Or the frenzy around smart luggage with built-in GPS tracking?
Both captured major industry attention a few years ago, yet failed to achieve lasting impact.
Meanwhile, others—like Advanced Air Mobility and the metaverse—have been heavily hyped but remain far from realistic mainstream adoption in the near-term future, while technologies like autonomous driving have taken far longer to materialize than initially projected.
And then, of course, there are the true game-changers—Generative AI being the latest example of a technology that isn’t just another passing trend but a long-term industry disruptor.
For anyone working in innovation, digital transformation, or the startup investment world, the challenge is the same: how do you distinguish between hype and real technological shifts? Day in and day out, businesses must determine which trends deserve their mental bandwidth (and investment)—and which will ultimately fizzle out. This is particularly true in Travel and Mobility Tech, where missing out on key innovations can mean falling behind the competition.
At the Lufthansa Innovation Hub, this is a challenge we wrestle with constantly (and a key reason why Lufthansa established us as a standalone innovation unit).
- A few months ago, we started developing a framework to help cut through the noise—one that differentiates between trends that are overhyped (all talk, little progress) and those that are underrated (flying under the radar but with strong potential for high ROI).
- Today, we’re introducing the first version of this framework. It’s still a work in progress, and we plan to refine it further with industry input.
But for now, we’re putting it to the test—applying it to the aviation industry to assess the real potential behind eight major air travel technologies.
Methodology: Separating Talk from Action
Before diving into the key trends shaping the future of aviation, let’s first break down the methodology behind our framework.
Our goal is simple: to distinguish overhyped trends from underrated ones by assessing two key factors—how much public attention they receive (TALK) versus how much real technological progress is being made (ACTION).
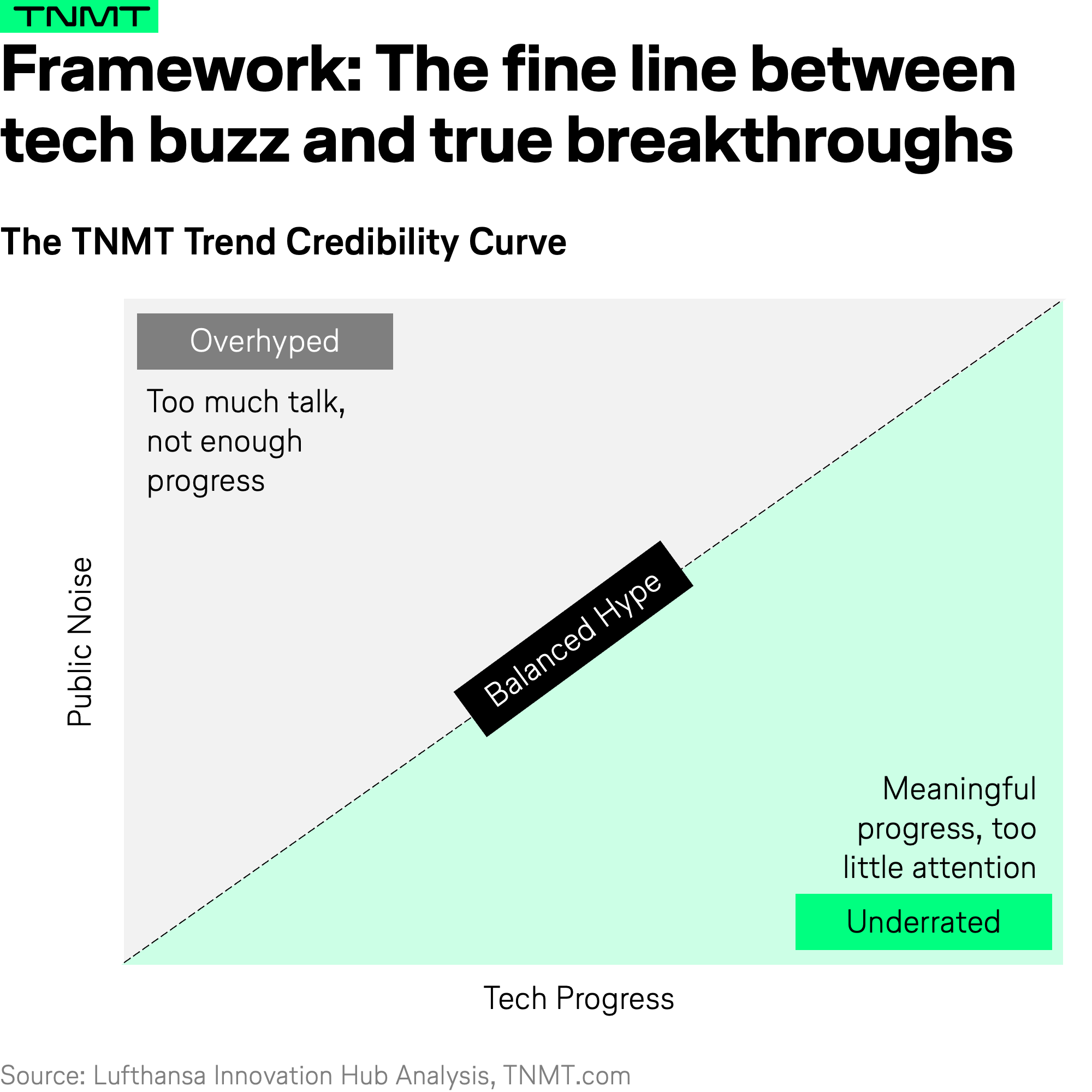
Take Generative AI as an example.
- There’s no shortage of public debate surrounding GenAI—every day, headlines claim its potential to revolutionize productivity, reshape industries, and transform the way people search for and book travel.
- But crucially, this hype is backed by real technological progress. Large Language Models (LLMs) are improving at an unprecedented rate, with continuous advancements in model architecture, efficiency, and real-world applications.
In this case, the high level of talk is arguably justified by equally significant action—placing GenAI within what we call the Balanced Hype zone, where industry noise aligns with tangible innovation.
How We Quantify Public Noise vs. Technological Progress
To compare trends in a quantifiable way, we needed to assign concrete numerical values to both variables.
Here’s how we did that:
- Public Noise (Talk): We measure mainstream hype using Google Search results, which serve as a proxy for how much public discourse surrounds a trend in a given year.
- Technological Progress (Action): We track the total number of patents and academic papers published annually (sourced from Lens.org) as indicators of actual scientific and technical advancements. While not a perfect measure, this approach provides a strong signal of real innovation activity.
Applying the TNMT Tech Hype Balance to Aviation
To apply this framework to aviation, we analyzed a selection of technologies—those previously covered in our Gartner Hype Cycle Analysis—tracking their development over the past five years.
To ensure comparability, we normalized both variables on a scale from 0 to 1, where:
- 0 represents the lowest cumulative value (least attention or development).
- 1 represents the highest cumulative value (most attention or development).
This normalization allows us to map trends on a consistent scale, regardless of their original magnitude.
The result?
A visual mapping of key aviation trends based on their Trend Credibility, with each trend’s trajectory plotted over a five-year period.
This structured approach helps us spot patterns, track shifts, and identify which technologies may be over- or under-prioritized by industry players.
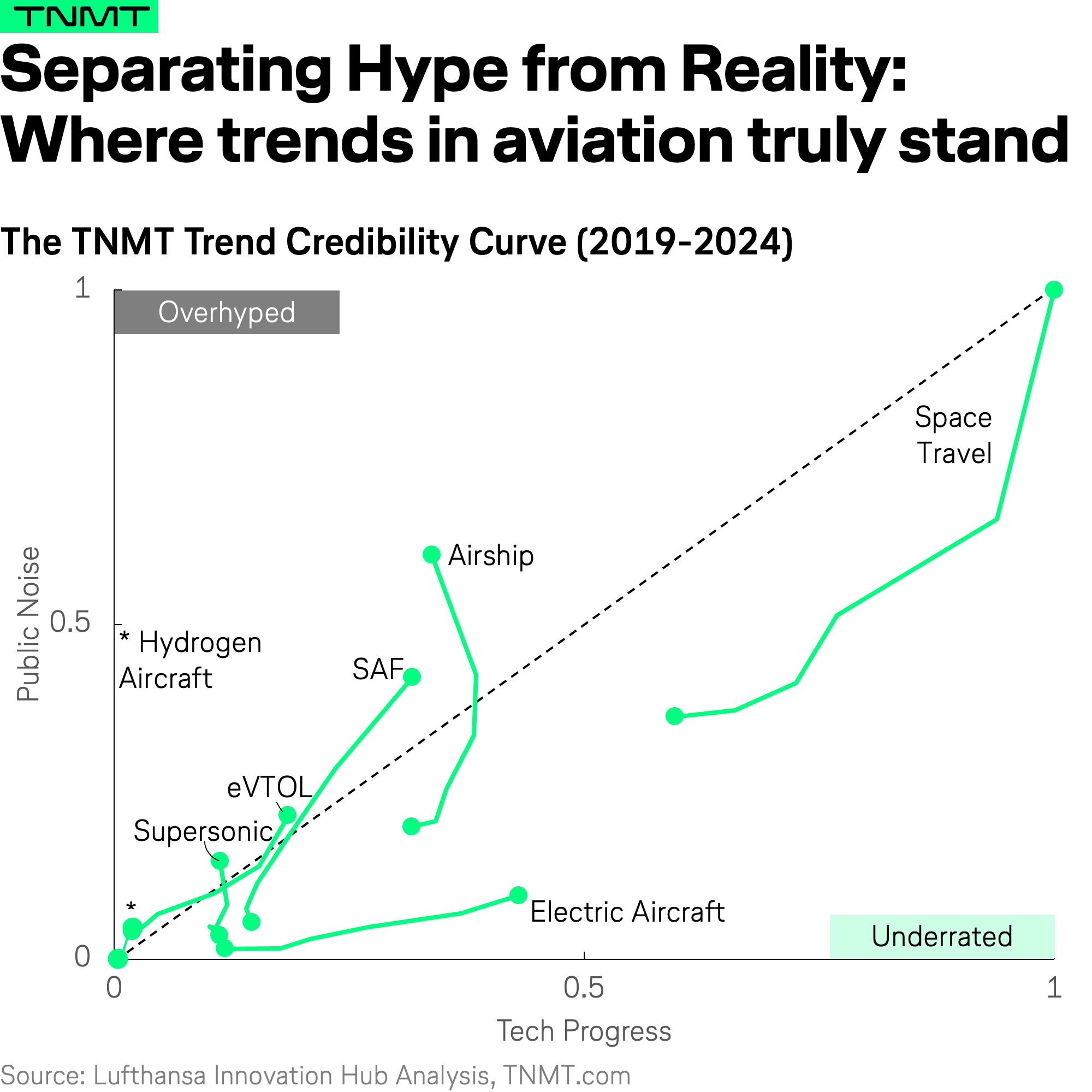
Hype vs. Reality: What the Data Reveals
As you can see in the visual above, our hypothesis holds true.
- Some trends receive disproportionate media attention but show little real technological progress—suggesting they are more hype than substance.
- Others follow a more balanced trajectory, where engineering advancements keep pace with media interest, signaling genuine potential for long-term impact.
- And then there are the underrated trends—those flying under the radar, where technological progress outpaces public attention, making them far more real and relevant than most people realize.
Let’s take a closer look at all seven trend lines individually, starting with the underrated ones.
Trend #1: Space Travel – Big Dreams, Bigger Breakthroughs
Space travel—at least in the context of passenger voyages—still feels like a distant dream (except for a few billionaires). But when looking at space technology as a whole—including rocket launches for satellite and research missions—the data tells a different story.
- It is one of the most technologically advanced sectors in transportation today. While space travel receives the highest media attention among all trends we analyzed, this hype is fully justified by genuine breakthroughs.
- Unlike many overhyped technologies (which we’ll discuss further below), space travel’s technological progress has long outpaced media buzz, making it a prime example of an underrated but high-impact innovation—one that has recently reached its balance point in 2024.
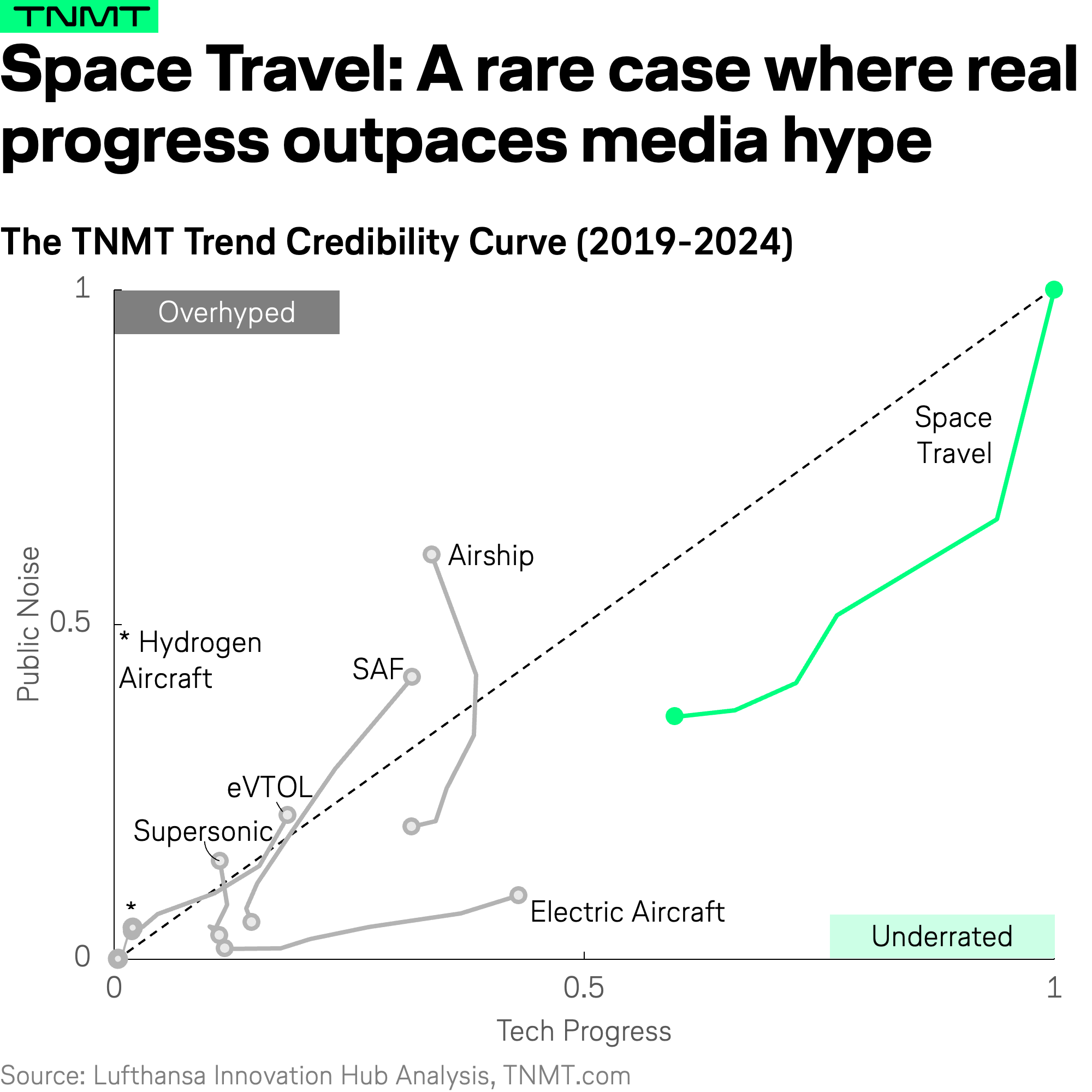
Space travel’s technological advancements are not a recent phenomenon.
- By 2019, patent and research output had already reached 0.66, meaning real-world progress was well underway before public hype accelerated.
- This period saw major breakthroughs in reusable rocket technology, led by SpaceX’s Falcon 9 landings, alongside a surge in private-sector investment, with players like Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic pushing for commercial spaceflight.
- NASA’s Artemis program, designed to return humans to the Moon, further reinforced scientific momentum.
Given all these major developments, media attention grew steadily, driven by tangible milestones rather than speculative hype.
Then, in 2023, technological progress spiked, aligning with further advancements that proved the sector’s viability.
- SpaceX’s Crew Dragon missions cemented private-sector involvement in astronaut transport, while suborbital space tourism became a reality with successful commercial flights from Blue Origin and Virgin Galactic.
- The Moon returned to focus, with NASA’s Artemis I mission laying the groundwork for human exploration, and Firefly Aerospace achieving a successful lunar landing in early 2025.
As a result, media attention surged from 0.65 to 1.00, fully reflecting the sector’s rapid progress.
We conclude: Despite its sci-fi-like perception, space travel is one of the most technologically mature trends in aviation today—a rare case where hype is fully matched by real-world innovation.
Trend #2: Electric Aircraft – Silent Progress, Powerful Potential
Electric aircraft is the second underrated trend in our analysis. Unlike many aviation technologies that generate more headlines than tangible progress, electric aviation has been steadily maturing in the background while remaining largely underhyped.
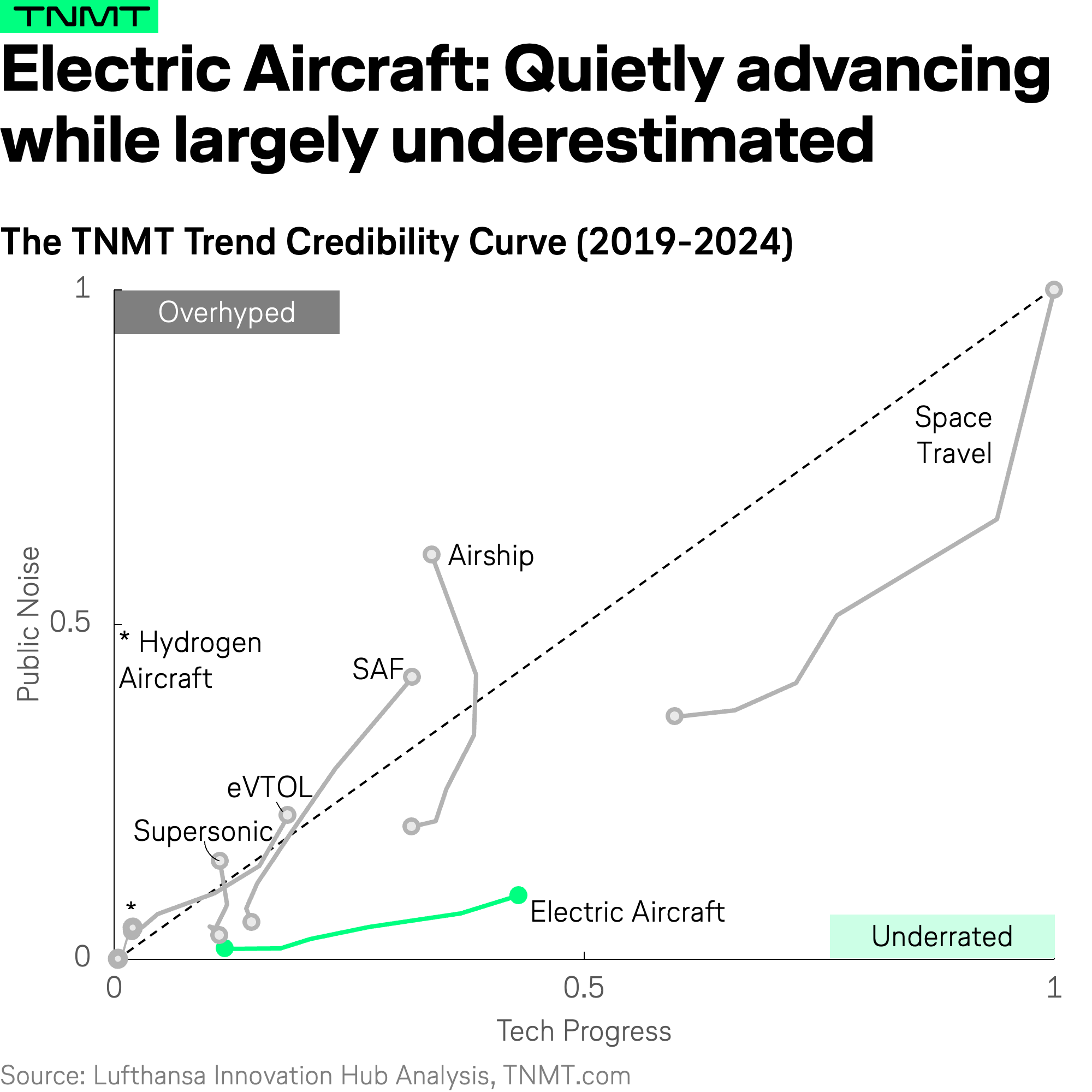
Our data shows that engineering progress in this sector has grown more than 3.5 times from 2019 to 2024, yet media attention remains relatively low. This engineering progress is largely driven by patent activity, which highlights a shift from foundational to advanced research–a clear sign that the industry is moving beyond early-stage experimentation towards certification.
To give a few examples:
- Battery technology patents related to aviation have surged by 200% since 2021, focusing on energy density, charging speed, and thermal management.
- Aerodynamics and lightweight materials patents nearly doubled since 2020, signaling efforts to extend range through efficiency, not just propulsion improvements.
- Electric propulsion system patents grew by 150% from 2021 to 2023, reflecting a transition from early-stage R&D to certifiable commercial powertrains.
- Meanwhile, air traffic integration and automation patents also surged by 300% from 2022 to 2024, showing that regulators and infrastructure players are actively preparing for electric aircraft to enter existing aviation systems.
All these advancements are already translating into real-world test flights, setting the stage for broader market adoption down the road (at least on short-haul routes). Case in point: Heart Aerospace, Maeve, and Vaeridion are progressing toward finalizing their concepts, while airlines such as Air Napier, United Airlines, and Air Canada have placed firm aircraft orders—shifting electric aviation from concept to tangible market demand.
The conclusion is clear: electric aviation is quietly emerging as one of the most technologically advanced sectors in the industry, laying the groundwork for large-scale adoption in the future.
From Underrated to Overhyped: The Shifting Hype Cycle
With the truly underrated technologies out of the way, it’s time to shift focus to a different category—aviation trends that started as underappreciated innovations but have now crossed into overhyped territory.
These are technologies that once flew “under the radar”, driven by solid engineering advancements, but have recently seen a surge in media attention that outpaces real-world progress.
Four trends fit this pattern: Airships, Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF), Supersonic Aircraft, and Hydrogen Aircraft.
Let’s take a closer look at their trajectories.
Trend #3: Airships – Floating on Hype, Grounded by Reality
The airship industry has seen a recent surge in media attention, but little technological progress to back it up. While engineering development has remained flat over the past five years, media mentions have tripled—suggesting a disconnect between hype and real innovation.
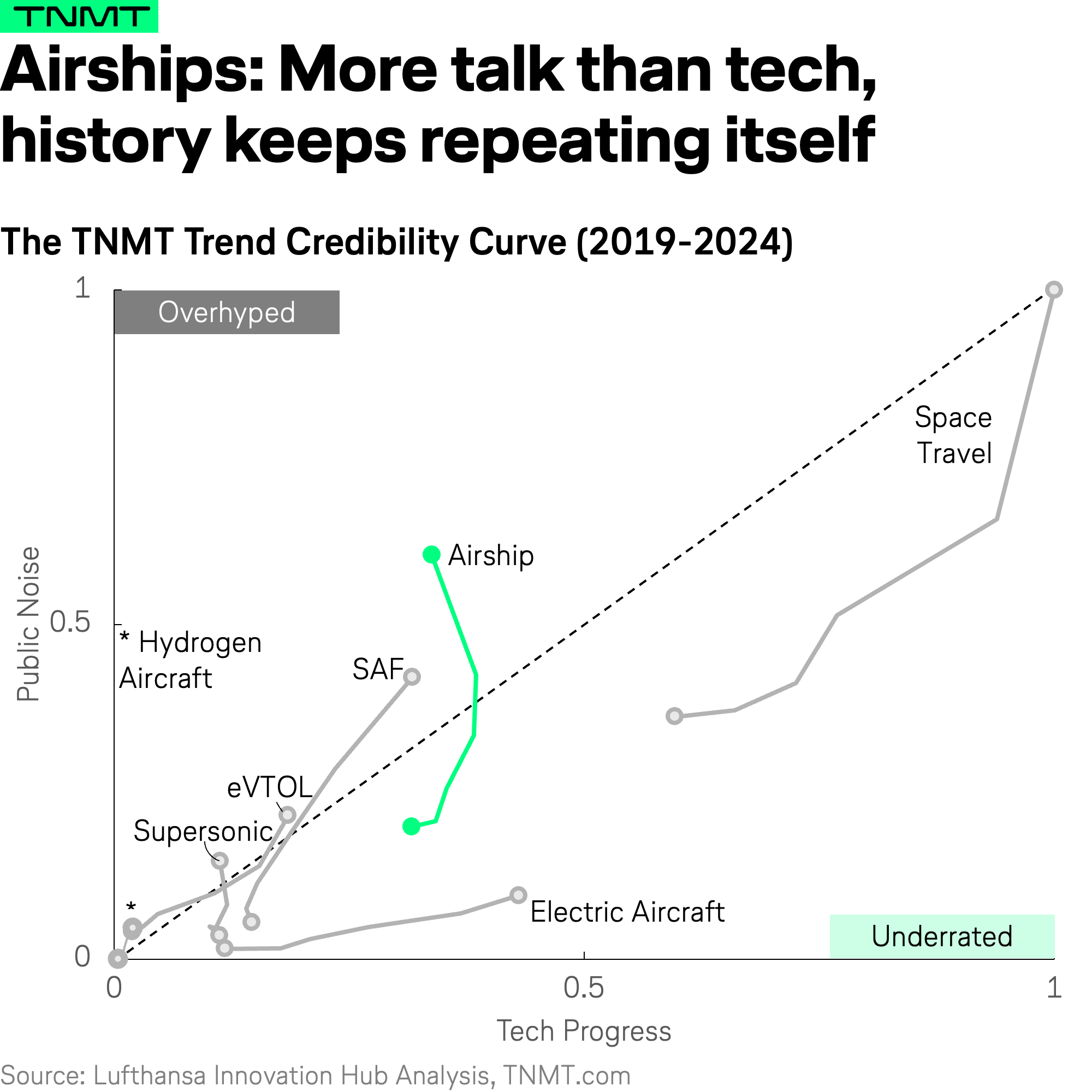
Patent data confirms this stagnation. Rather than groundbreaking advancements, most filings since 2019 focus on incremental optimizations rather than true reinvention—a predictable trend given that the concept of today’s airships have existed for over 150 years.
- 40% of patent filings since 2019 address structural tweaks and efficiency improvements rather than new designs.
- 25% focus on wireless communication and automation, aiming to integrate airships into aviation systems rather than making them a standalone solution.
- Most notably, less than 10% explore propulsion breakthroughs, meaning there’s no imminent shift toward high-speed, high-efficiency airships.
A prime example is Hybrid Air Vehicles’ Airlander 10, widely promoted as a sustainable aviation solution. Despite years of press coverage, it has yet to enter service, secure regulatory approvals, or demonstrate a clear real-world use case beyond promotional tours.
Our take: airships are mostly noise—an idea that keeps resurfacing but lacks meaningful potential for the future of aviation.
Trend #4: SAF – High Expectations, Limited Execution
SAF has long been positioned as aviation’s key solution for reducing emissions.
Early technological progress supported this promise, but since 2022, public expectations have outpaced real-world deployment. While media attention and regulatory discussions have surged, SAF production capacity has struggled to keep pace, making it one of the most overhyped trends in aviation today.
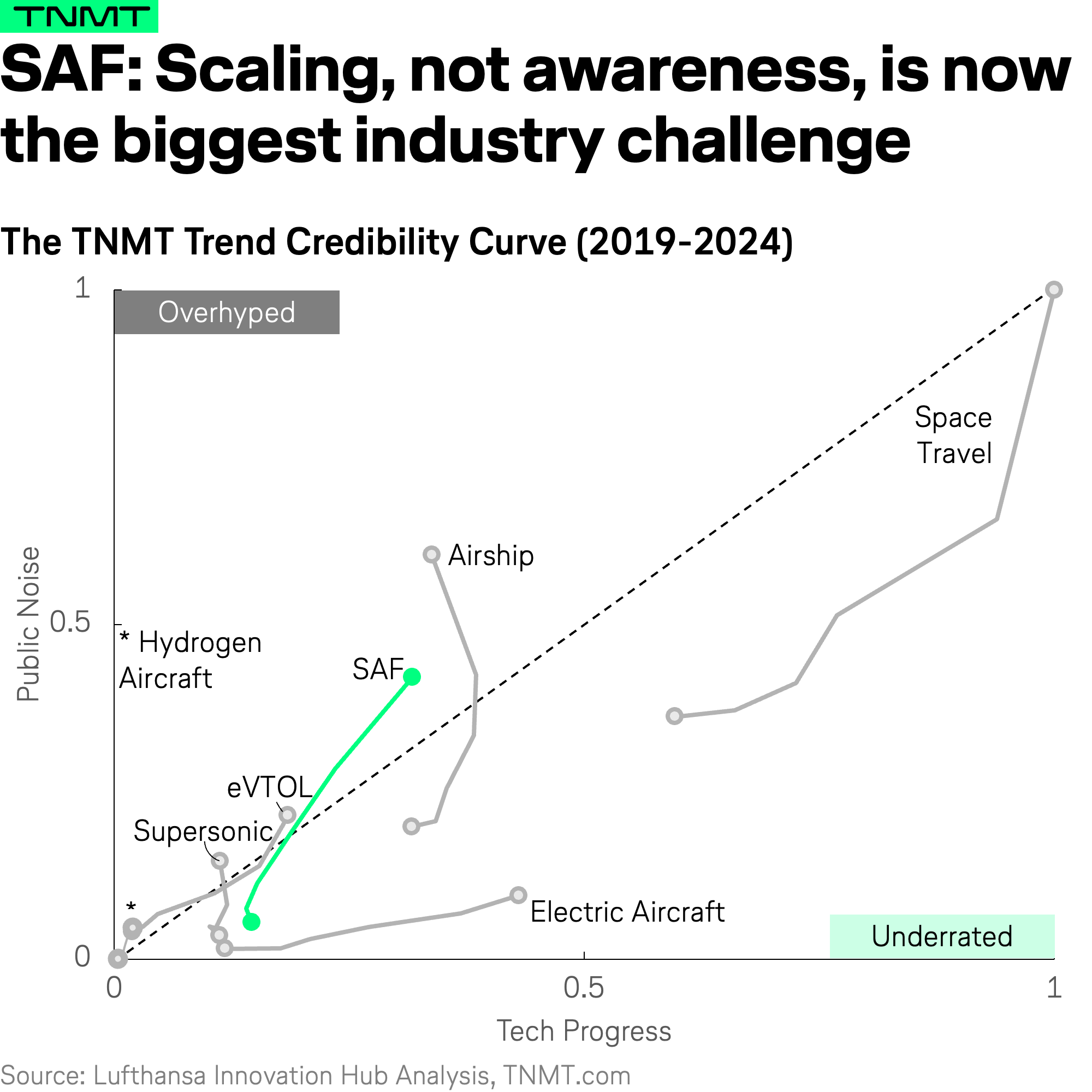
This growing gap between expectation and execution is largely fueled by:
- Publicly announced airline net-zero commitments, such as IATA’s 2050 goal.
- Government mandates and incentives, including the EU’s Fit for 55 plan, CORSIA, ReFuel EU Aviation, and the U.S. Inflation Reduction Act’s SAF tax credits.
- Corporate sustainability pushes, with companies like BCG, McKinsey, Microsoft, and Amazon investing in SAF to meet emissions targets.
The takeaway: SAF has a proven technological foundation, but large-scale deployment remains its biggest hurdle. Its true adoption depends on scaling production and achieving cost competitiveness with fossil fuels—challenges that remain largely unsolved thus far.
Trend #5: Supersonic – Speeding Through Hype, Stalling in Reality
Supersonic travel remains a niche trend in aviation, as reflected in our Trend Credibility Curve framework, where it sits in the bottom left corner—indicating a small trend line with limited progress. While media attention has surged, technological advancements have barely moved, making supersonic one of the clearly overhyped trends in aviation today.

In 2024 alone, media coverage jumped by over 70%, fueled by high-profile announcements from Boom Supersonic and NASA’s X-59 program, despite the absence of a commercially viable aircraft.
- A rare milestone came in January 2025, when Boom Supersonic’s XB-1 successfully hit supersonic speeds without generating a disruptive sonic boom.
- While a notable step, it did little to resolve the fundamental challenges stalling supersonic travel—high operating costs, strict regulations, and unresolved efficiency concerns.
Beyond technological feasibility, the business case remains highly questionable—something we previously analyzed in TNMT. Historically, supersonic flight has struggled with prohibitively high costs, limited route viability, and environmental concerns, making widespread adoption unlikely.
In short: Supersonic travel may continue to generate headlines, but its long-term viability—both technologically and financially—remains far from certain.
Trend #6: Hydrogen Aircraft – Lofty Promises, Little Lift
Hydrogen aircraft has been a widely discussed concept in aviation—particularly within sustainability circles—but real-world progress remains minimal. Unlike other emerging trends like SAF, it never had an underrated phase—from the start, media hype has exceeded technological advancements, creating a narrative that far outpaces actual feasibility.

As the visual shows, its trend line is weak, reflecting limited progress in both public interest and engineering development. Technological advancements have been incremental at best, with no major breakthroughs in hydrogen production, storage, or aircraft integration.
The biggest hurdle?
- Fundamental technological challenges remain unsolved, and many experts outright reject hydrogen as a viable solution for commercial aviation.
- A clear sign of this reality: Airbus recently “paused” (effectively canceled) its ZEROe hydrogen aircraft concept, and Universal Hydrogen—one of the key players in this space—went bankrupt last year.
In short: hydrogen aircraft continues to receive public attention, but its path to large-scale viability remains highly uncertain—some might say, delusional.
The Final Trend #7: A Surprising Balance–Or a Model Limitation?
After analyzing trends that are either overhyped or underrated, we now turn to a category that defies expectations. eVTOLs (electric Vertical Takeoff and Landing aircraft) stand out as a rare case where hype and technological progress appear mostly aligned—at least according to our framework.
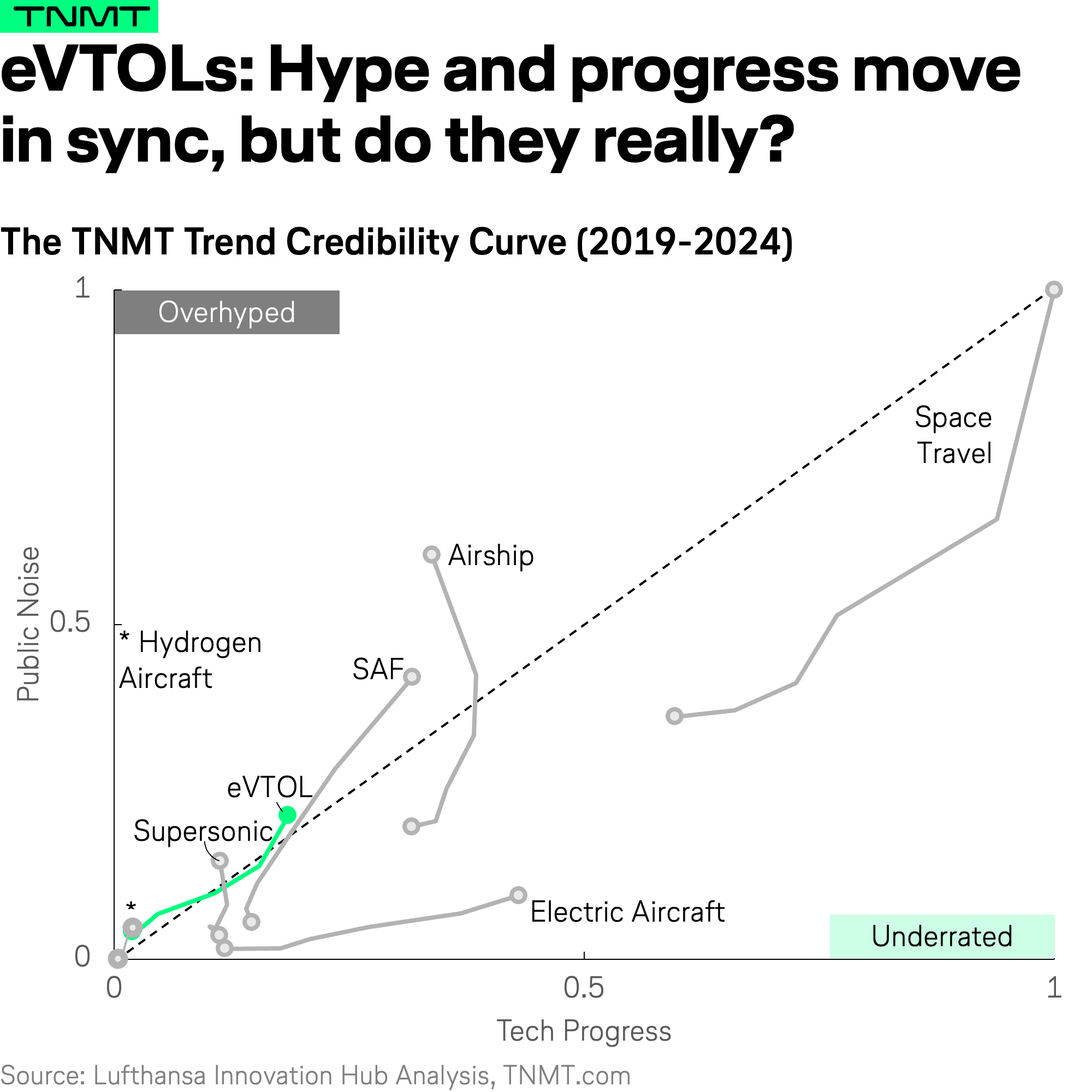
At first glance, the eVTOL trend moves remarkably well along the Balanced Hype Diagonal, suggesting a sector developing at a healthy pace. Given the recent turbulence in the industry, with companies like Lilium and Volocopter on the brink of shutting down, one might have expected a far more negative trajectory.
However, we believe this “balanced” trend line does not fully reflect reality—it actually highlights a limitation of our current Trend Credibility model.
- Our framework relies on only two input variables—media attention and technological progress—which, in the case of eVTOLs, fail to capture critical external factors that shape the industry’s future.
- As we outlined in our 2024 deep dive into the Advanced Air Mobility (AAM) sector, eVTOLs still face massive hurdles beyond engineering advancements—particularly in business model viability, funding sustainability, regulatory approvals, and infrastructure readiness.
In short: eVTOLs have made significant technical progress, but their long-term viability depends on far more than just engineering breakthroughs. Factoring in these additional challenges, the sector’s near-term future looks increasingly shaky. This is an important reminder that our Trend Credibility framework still needs refinement to become a truly reliable decision-making tool.
Closing Thoughts: Separating Hype from Reality in Aviation Innovation
With this analysis, we set out to provide a practical tool for innovation managers and decision-makers—not just in aviation, but across industries—to differentiate noise from signal and make smarter investment decisions. While our Trend Credibility model is not perfect, it has already proven valuable in identifying which trends are truly shaping the future of aviation and which are running on empty hype.
Looking at aviation trends in particular, the framework has brought several critical insights to light. Space technologies and electric aircraft emerged as underrated fields, with real technological progress outpacing public perception. The latter, in particular, is a mission-critical innovation for aviation professionals to monitor—even if mass-market adoption of electric flying is still years away.
Meanwhile, our framework reinforces that for trends like SAF, the key bottleneck is no longer public acceptance but real technological progress—specifically, the ability to scale production capacity. On the other hand, airships and hydrogen aircraft appear increasingly overhyped, with limited technological breakthroughs to sustain long-term momentum. These trends risk fading into irrelevance sooner than later.
This is just the beginning. If you have insights or recommendations on how to improve our Trend Credibility Curve, we’d love to hear from you.
Let’s keep refining how we separate hype from real progress—because in aviation, betting on the right innovations will soon make all the difference.